Divided Differences
-
- What?
- A recursive method definition used to successively generate the approximating
polynomials.
- Form of the Polynomial:
- \[P_n(x) = a_0 + a_1(x − x_0) + a_2(x − x_0)(x − x_1) +···+ a_n(x − x_0)···(x − x_{n−1}),\ \ \ (3.5)\]
-
Evaluated at \(x_0\): \(\ P_n(x_0) = a_0 = f(x_0)\)
-
Evaluated at \(x_1\): \(\ P_n(x_1) = f(x_0) + a_1(x_1 − x_0) = f(x_1)\)
-
\(\implies \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ a_1 = \dfrac{f(x_1) − f(x_0)}{x_1 − x_0}\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ (3.6)\).
- The divided differences:
- The zeroth divided difference of the function f with respect to \(x_i\):
- Denoted: \(f[x_i]\)
- Defined: as the value of \(f\) at \(x_i\)
-
\(f[x_i] = f(x_i) \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ (3.7)\).
-
The remaining divided differences are defined recursively.
- The first divided difference of \(f\) with respect to \(x_i\) and \(x_{i+1}\):
- Denoted: \(f[x_i,x_{i+1}]\)
- Defined: as
-
\(f[x_i,x_{i+1}] = \dfrac{f[x_{i+1}] − f[x_i]}{x_{i+1} − x_i} \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ (3.8)\).
- The second divided difference of \(f\) with respect to \(x_i\), \(x_{i+1}\) and \(x_{i+2}\):
- Denoted: \(f[x_i,x_{i+1},x_{i+2}]\)
- Defined: as
-
\(f[x_i,x_{i+1},x_{i+2}] = \dfrac{f[x_{i+1},x_{i+2}] − f[x_i,x_{i+1}]}{x_{i+2} − x_i} \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ (3.85)\).
- The Kth divided difference of \(f\) with respect to \(x_i\), \(x_{i+1},...,x_{i+k-1},x_{i+k}\):
- Denoted: \(f[x_i,x_{i+1},...,x_{i+k-1},x_{i+k}]\)
- Defined: as
-
\[f[x_i,x_{i+1},...,x_{i+k-1},x_{i+k}] = \dfrac{f[x_{i+1},x_{i+2},...,x_{i+k}] − f[x_i,x_{i+1},...,x_{i+k-1}]}{x_{i+k} − x_i} \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ (3.9)\]
-
The process ends with the nth divided difference
- The nth divided difference of \(f\) with respect to \(x_i\), \(x_{i+1},...,x_{i+k-1},x_{i+k}\):
- Denoted: \(f[x_0,x_1,...,x_n]\)
- Defined: as
-
\(f[x_0,x_1,...,x_n] = \dfrac{f[x_1,x_2,...,x_n] − f[x_0,x_1,...,x_{n-1}]}{x_n − x_0} \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ (3.95)\).
- The zeroth divided difference of the function f with respect to \(x_i\):
-
The Interpolating Polynomial:
\(P_n(x) = f[x_0] + f[x_0, x_1](x − x_0) + a_2(x − x_0)(x − x_1)+···+ a_n(x − x_0)(x − x_1)···(x − x_{n−1})\) - Newton’s Divided Difference:
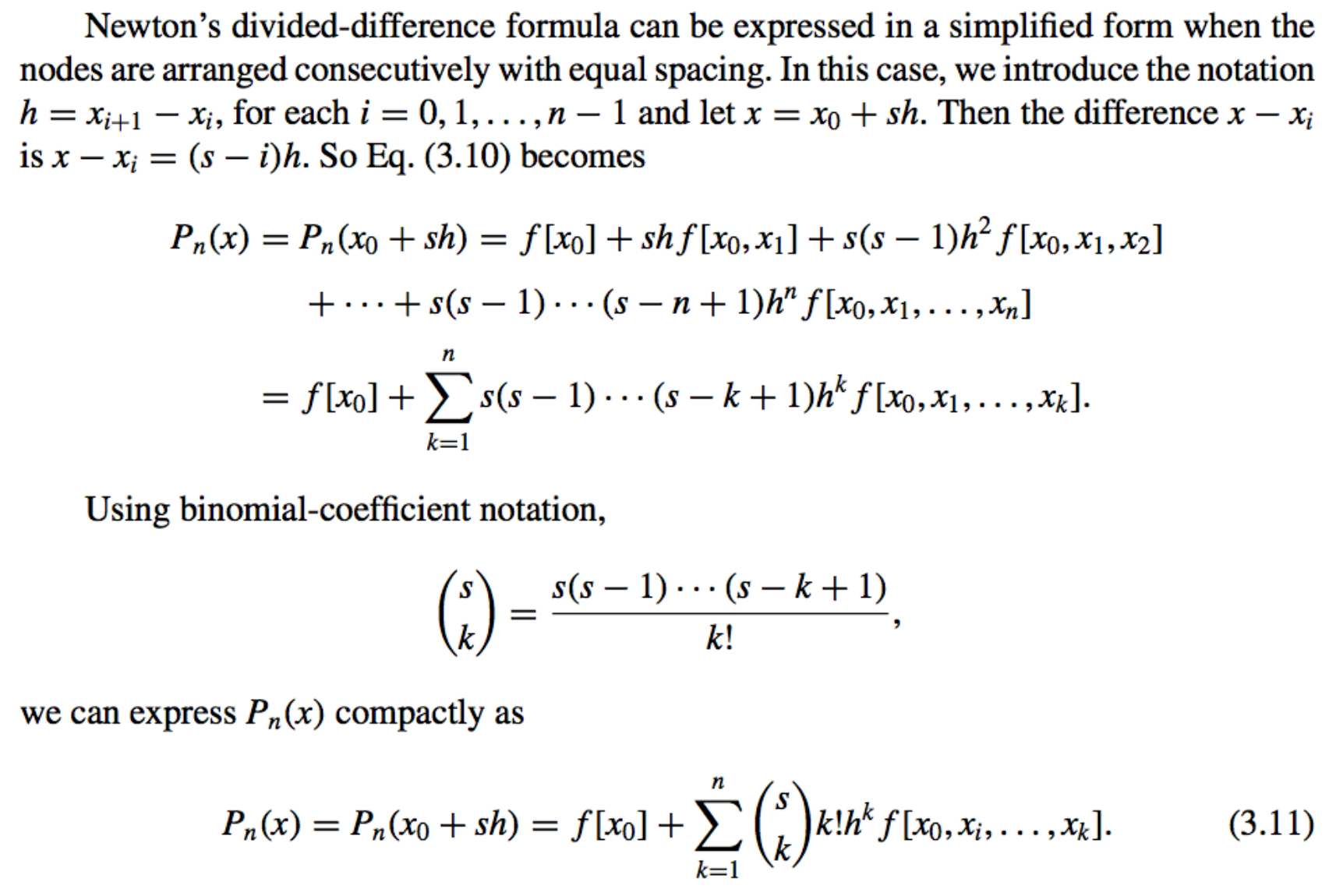
\(P_n(x) = f[x_0]+ \sum^n_{k=1}f[x_0, x_1, ... , x_k](x-x_0)···(x − x_{k−1}) \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ (3.10)\)The value of \(f[x_0,x_1,...,x_k]\) is independent of the order of the numbers \(x_0, x_1, ... ,x_k\)
- Generation of Divided Differences:
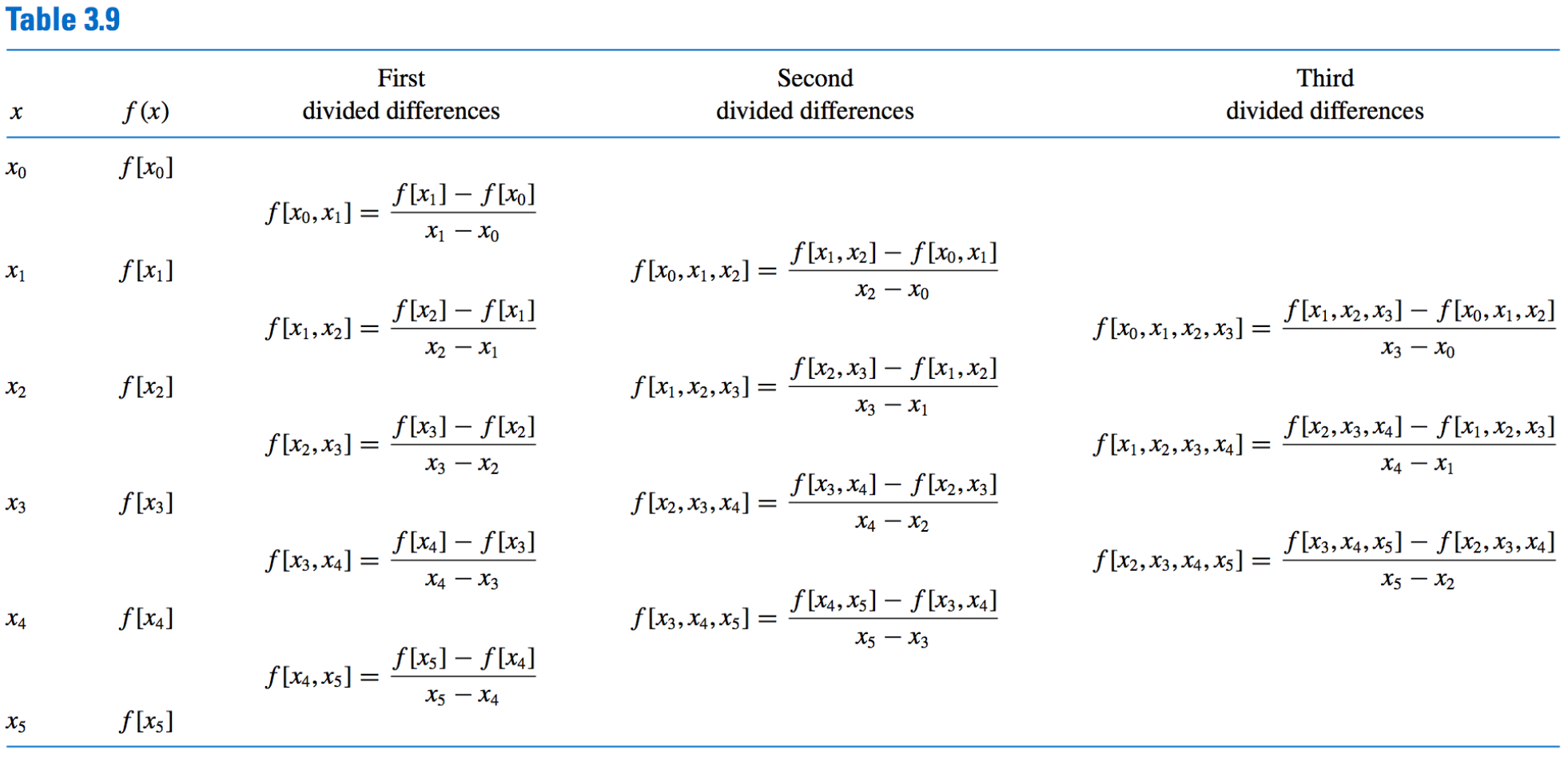
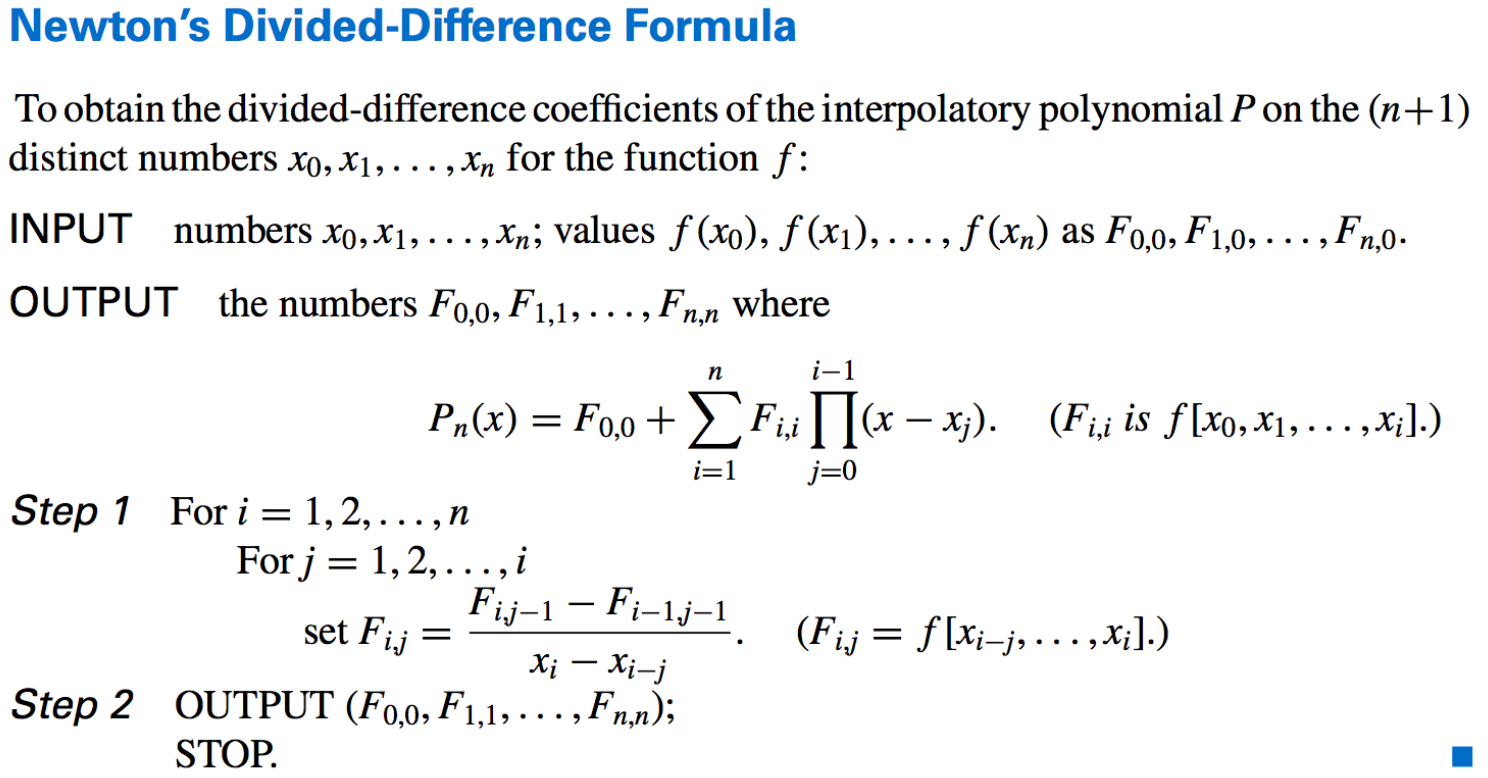
- Algorithm:
Forward Differences
- Forward Difference:
- The divided differences (with del notation):
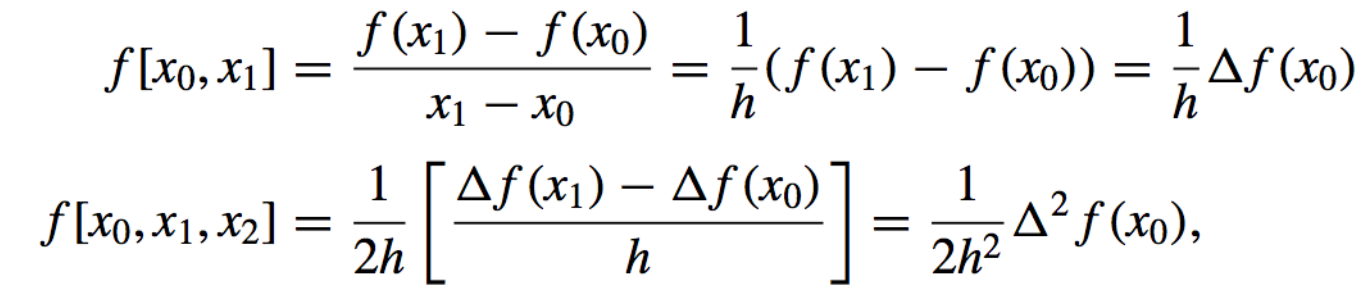
and in general,
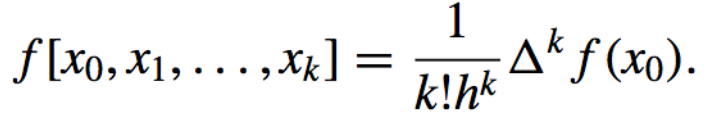
-
Newton Forward-Difference Formula:
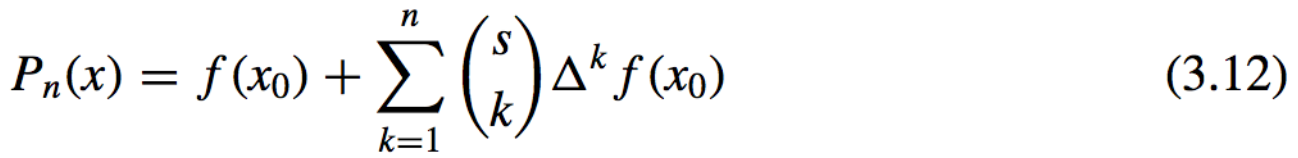
Backward Differences
-
Backward Difference:
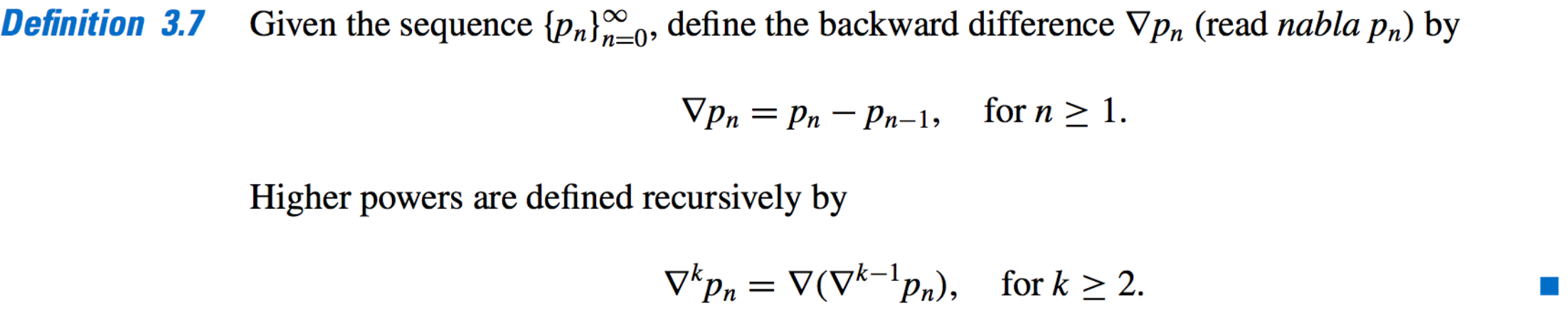
- The divided differences:
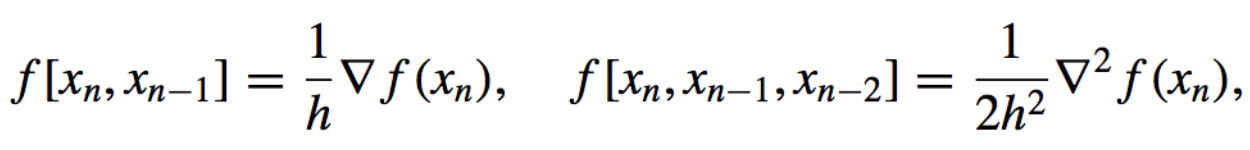
and in general,
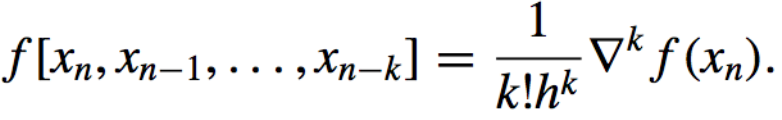
Consequently, the Interpolating Polynomial
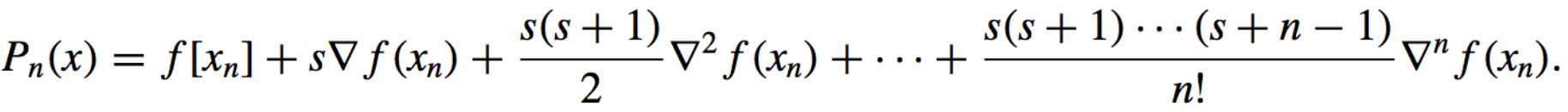
If we extend the binomial coefficient notation to include all real values of s by letting
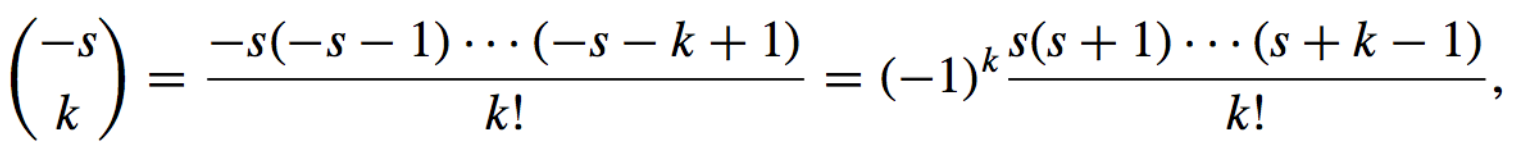
then
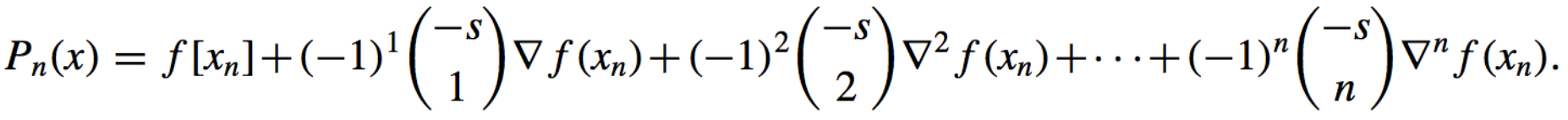
- Newton Backward–Difference Formula:
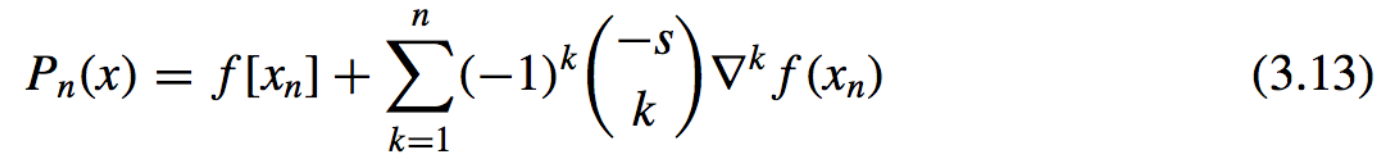
Centered Differences
-
What?
-
- Why?
- The Newton forward- and backward-difference formulas are not appropriate for
approximating \(f(x)\) when x lies near the center of the table because neither will permit the highest-order difference to have \(x_0\) close to x.
- Stirling’s Formula:
- If \(n = 2m + 1\) is odd:
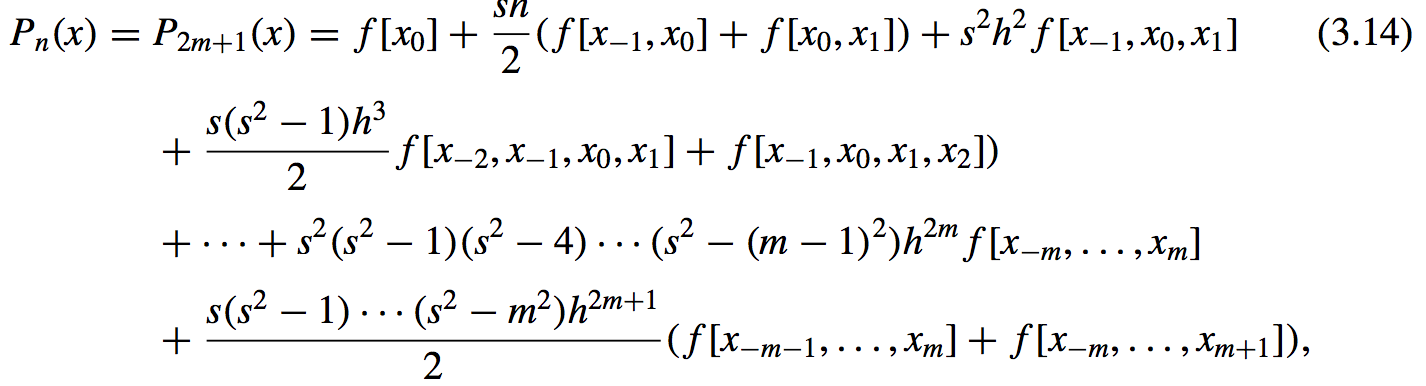
- If \(n = 2m\) is even: [we use the same formula but delete the last line]
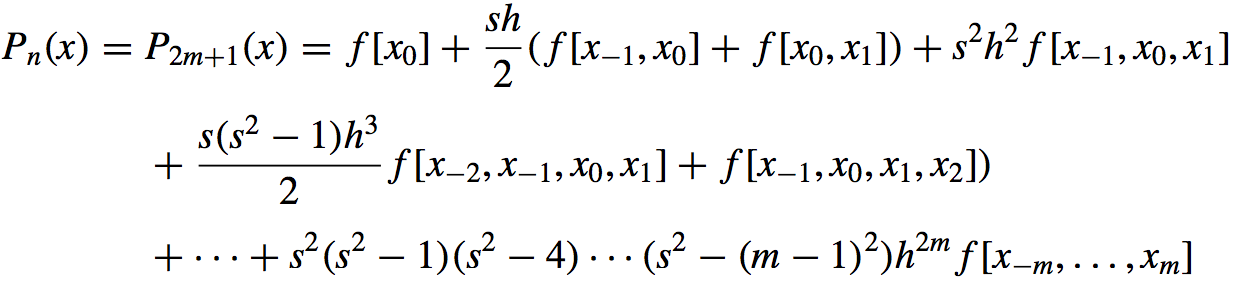
- If \(n = 2m + 1\) is odd:
-
Table of Entries:
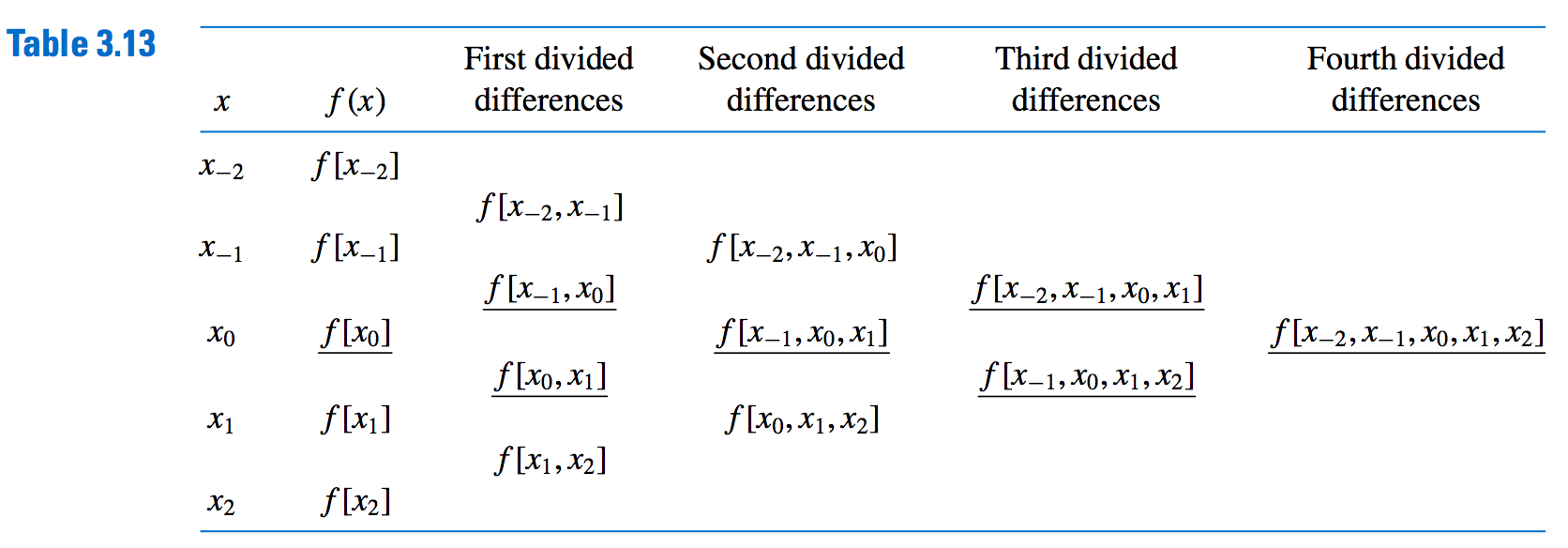
- OMG:
\(F_{i,j} = \dfrac{1}{x_{i} − x_{i-j}}[(F_{i,j-1} − F_{i-1,j-1})] \\ Q_{i,j} = \dfrac{1}{x_{i} − x_{i-j}}[Q_{i,j-1} − Q_{i-1,j-1}], \\\)
